TL;DR: What Does a GTM Engineer Do?
GTM (Go-to-Market) engineers bridge sales, marketing, and technical teams to build automated, scalable revenue systems.
Key responsibilities include integrating tech stacks, automating workflows, ensuring data quality, and aligning cross-team operations.
Essential skills: CRM mastery, automation, analytics, business strategy, and strong communication.
GTM engineers are in high demand for their ability to drive efficient, repeatable growth.
A typical day involves syncing with teams, optimizing workflows, experimenting, reporting, and solving integration challenges.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital marketplace, companies need to connect sales, marketing, and technology more seamlessly than ever. Enter the GTM engineer—a new breed of hybrid professional who’s transforming how organizations drive revenue and scale growth. But what does a GTM engineer do? This article unpacks the GTM engineer role, their responsibilities, the skills you need to succeed, and what a typical day looks like. Whether you’re considering this career path or looking to hire your first GTM engineer, read on to learn why this role is quickly becoming indispensable.
What Is a GTM Engineer?
A GTM (Go-to-Market) engineer is a technical strategist who bridges the gap between sales, marketing, and operations, ensuring these teams work together efficiently to drive revenue. Unlike traditional roles that often operate in silos, GTM engineers architect and automate the systems that power every stage of the customer journey—from first touch to renewal.
At its core, the GTM engineer role is about engineering scalable, repeatable growth. GTM engineers blend technical know-how (think automation, data pipelines, CRM mastery) with business acumen, enabling sales and marketing teams to operate at peak efficiency. They’re not just software developers or data analysts; they’re revenue architects who turn go-to-market strategies into reality.

GTM Engineer Responsibilities: Beyond Traditional Operations
What are the key GTM engineer responsibilities? Here's what sets them apart from classic RevOps, SalesOps, or MarketingOps:
1. Building and Optimizing Revenue Systems
Architecting lead qualification, scoring, and routing workflows.
Designing seamless omnichannel campaigns that unite email, social, ads, and more.
Automating sales support—feeding reps the right info at the right time.
2. Integrating and Managing the Tech Stack
Connecting CRMs (like Salesforce or HubSpot) with marketing and analytics tools.
Implementing and optimizing automation platforms (such as Zapier, n8n, or custom scripts).
Ensuring clean, enriched, and connected data across all platforms.
3. Automating Workflows and Data Pipelines
Setting up automated data enrichment for leads and accounts.
Building real-time notifications and alerts for sales teams (e.g., when a prospect revisits a proposal).
Automating post-sale expansion and churn-prevention campaigns.
4. Driving Alignment Across Teams
Breaking down silos between sales, marketing, and customer success.
Creating dashboards that give leadership a single source of truth on pipeline health.
Ensuring cross-team workflows are efficient and data-driven.
5. Experimenting and Scaling What Works
Rapid prototyping of new GTM workflows (e.g., new outbound strategies, automated partner sourcing).
Measuring, iterating, and scaling successful experiments across the organization.
GTM Engineer Skills: What Makes a Great GTM Engineer?
Because the GTM engineer role is so cross-functional, it requires a unique blend of GTM engineer skills:
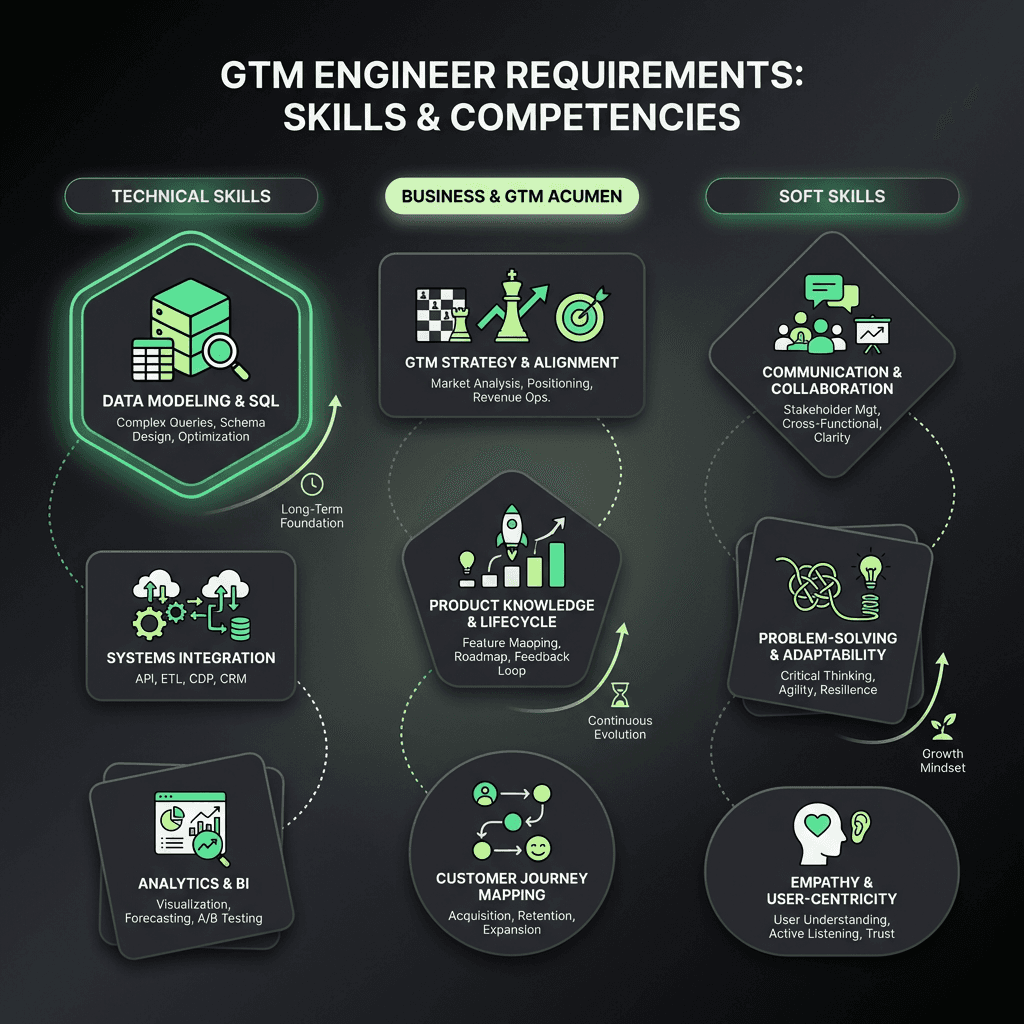
Technical Skills
CRM Mastery: Deep experience with Salesforce, HubSpot, Marketo, etc.—customizing fields, automating workflows, and integrating third-party tools.
Automation & Integration: Comfortable with API integrations, low-code/no-code platforms, and basic scripting (Python, JavaScript, SQL).
Data Analytics: Ability to build reports, dashboards, and run data queries to spot trends and bottlenecks.
MarTech/SalesTech Fluency: Familiarity with the latest tools for data enrichment, lead generation, analytics, and outreach automation.
Business & Strategic Acumen
Go-to-Market Strategy: Understanding sales funnels, lead lifecycles, buyer personas, and customer success metrics.
Campaign Strategy: Partnering with marketers to design and execute targeted campaigns.
Sales Enablement: Translating sales team needs into actionable, automated solutions.
Soft Skills
Systems Thinking: Visualizing and optimizing the entire GTM system—not just isolated processes.
Cross-Functional Communication: Acting as a translator between technical and non-technical teams.
Curiosity & Experimentation: Comfort with rapid prototyping, A/B testing, and learning new tools fast.
Problem-Solving: Tackling complex, cross-team challenges with creative solutions.
Day in the Life of a GTM Engineer
So, what's a day in the life of a GTM engineer actually like? Here's a snapshot, based on common industry patterns:
Morning
Sync with Sales and Marketing: Review pipeline metrics, campaign performance, and any blockers.
Data Hygiene: Monitor automated jobs for CRM data enrichment and lead deduplication.
Tool Integration Checks: Ensure that all platforms (CRM, marketing automation, analytics) are syncing smoothly.
Midday
Workflow Optimization: Build or refine an automation—e.g., setting up a new lead scoring model or a Slack alert for high-intent website visitors.
Experimentation: Test a new outbound automation or AI-powered personalization script.
Reporting: Update dashboards, analyze funnel metrics, and flag any bottlenecks.
Afternoon
Cross-Functional Meetings: Collaborate with marketing on an upcoming campaign, or with customer success on automating expansion outreach.
Troubleshooting: Solve integration or workflow issues reported by team members.
Documentation: Record new automations, update SOPs, and share learnings with the team.
End of Day
Review KPIs: Check progress against revenue goals, pipeline health, and experiment results.
Plan Tomorrow's Sprints: Prioritize the next round of builds or experiments.
Why the GTM Engineer Role Is So Important (and in Demand)
The business world is shifting from manual, siloed operations to fully integrated, data-driven growth systems. GTM engineers are at the heart of this transformation. They:
Boost efficiency: Automate repetitive work so sales and marketing can focus on high-value tasks.
Enable scalability: Build revenue systems that grow with the business.
Drive alignment: Ensure every customer-facing team is working from the same playbook.
As a result, GTM engineers are commanding premium salaries and are highly sought after in SaaS, B2B, and fast-growing startups.
Conclusion: Is a GTM Engineer Right for Your Team (or Career)?
Whether you're a founder, sales leader, or aspiring GTM engineer, understanding this role is crucial for the future of go-to-market operations. GTM engineers are the architects behind modern, scalable revenue engines. They blend technical mastery with strategic insight, turning disconnected tools and workflows into a growth machine.
If you're looking for a high-leverage, high-impact career—or want to future-proof your company's revenue strategy—consider investing in GTM engineering. The payoff? Repeatable growth, cleaner data, and a team that's finally in sync.
FAQ: GTM Engineer Role & Career
1. What is a GTM engineer?
A GTM engineer is a hybrid technical and business role responsible for architecting and automating the systems and processes that drive an organization’s go-to-market (GTM) strategy, enabling seamless collaboration between sales, marketing, and operations.
2. What are the core responsibilities of a GTM engineer?
Core responsibilities include automating lead workflows, integrating CRMs with marketing and analytics tools, maintaining data quality, designing scalable campaigns, and driving cross-team alignment.
3. What skills are most important for a GTM engineer?
Key skills include expertise in CRM platforms, automation and integration (APIs, scripting, low-code tools), data analytics, business strategy, and effective cross-functional communication.
4. How does a GTM engineer differ from a traditional RevOps or SalesOps professional?
While RevOps or SalesOps often focus on specific departmental needs, a GTM engineer takes a holistic, technical approach to unifying and automating the entire revenue engine across sales, marketing, and customer success.
5. What industries hire GTM engineers?
GTM engineers are especially in demand at SaaS companies, B2B organizations, tech startups, and any business focused on scaling revenue through automated, data-driven systems.
6. What tools do GTM engineers typically use?
They typically work with CRMs (Salesforce, HubSpot), marketing automation tools (Marketo, Eloqua), integration platforms (Zapier, n8n), analytics tools (Looker, Tableau), and various data enrichment and outreach tools.
7. What does career growth look like for a GTM engineer?
GTM engineers can advance to leadership roles in Revenue Operations, become GTM architects, or move into broader business strategy, product management, or growth leadership positions due to their cross-functional expertise.
8. Why are GTM engineers becoming more important in modern organizations?
As businesses rely more on integrated, automated, and data-driven processes to scale, GTM engineers are crucial for breaking down silos, enabling rapid experimentation, and ensuring go-to-market strategies are executed efficiently.
References
Similar Posts

The Actually Easy Guide to Building Claude Skills

A Practical Guide to Building AI Workflows for B2B SaaS Marketing

25 Questions That Build a Real AI Marketing Strategy (Not Just an AI Stack)

Notion Agents vs Metaflow AI Agents: Building an AI Workflow That Works for You

How to Build AI Agents that actually gets stuff done

AI Content Repurposing with Customizable Prompts: Build Your Own Repurposing Tool with Metaflow AI

Account Intelligence Automation: How to Build AI Research Agents for ABM

Building AI Agents for Multi-Threading in ABM: Buying Committee Automation

How to Build an AI Intent Signal Aggregation Agent for ABM

AI Workflow Builder: How to Quickly Build Automated Growth Engines
SOLUTIONS
COMPARISON GUIDES
GET STARTED










