TL;DR:
AI agents are autonomous software entities that observe data, decide actions, and execute across your marketing stack to achieve specific tasks—moving beyond assistive AI and static automation.
Three core traits define AI agents: goal-driven behavior, autonomous cross-tool actions, and iterative learning that improves performance over time without manual recoding.
AI agents orchestrate your existing stack (CRM, MAP, analytics, product data) by reading signals, making decisions, and taking actions—while humans set goals, guardrails, and supervise outcomes with appropriate human oversight.
Practical use cases for B2B SaaS marketing include AI lead qualification & routing agents, AI lifecycle nurture agents for trials/freemium, and AI content distribution agents that optimize in real time.
Understanding how do AI agents work requires familiarity with large language models, task decomposition, and the ability of generative AI to handle complex tasks beyond natural language processing.
AI agents examples span from customer management and code generation to handling repetitive tasks across industries, demonstrating the versatility of agentic AI.
Key benefits: Reduced ops overhead, faster iteration cycles, higher funnel conversion, and more strategic marketers freed from manual workflow maintenance and task automation.
Manage risks by starting narrow, ensuring data quality, defining strict guardrails including security concerns, requiring explainability, and using human-in-the-loop approval for high-impact decisions.
Get started: Pick one high-leverage use case, define clear goals and constraints, map required data, design decision levers (not rigid workflows with predefined rules), launch in a small cohort, review weekly, and scale gradually.
Learning how to create an AI agent can be done through building from scratch or using specialized platforms—choose based on your team's technical resources and timeline.
Why B2B SaaS Marketers Suddenly Care About "AI Agents"
If you're a B2B SaaS marketer in 2026, you're probably drowning in tools—and somehow still drowning in manual work.
You have a CRM that tracks leads, a marketing automation platform that sends emails, analytics tools that measure everything, and product data flowing in from somewhere. Yet every day, you're still the human glue: copy-pasting data between systems, manually segmenting lists, updating lead scores in spreadsheets, and rebuilding workflows every time your ICP shifts or a campaign underperforms.
You've tried "AI-powered" features—the subject line generators, the predictive lead scoring models, the chatbots. They're helpful for isolated tasks, but they haven't fundamentally changed how much manual orchestration you're doing across your stack.
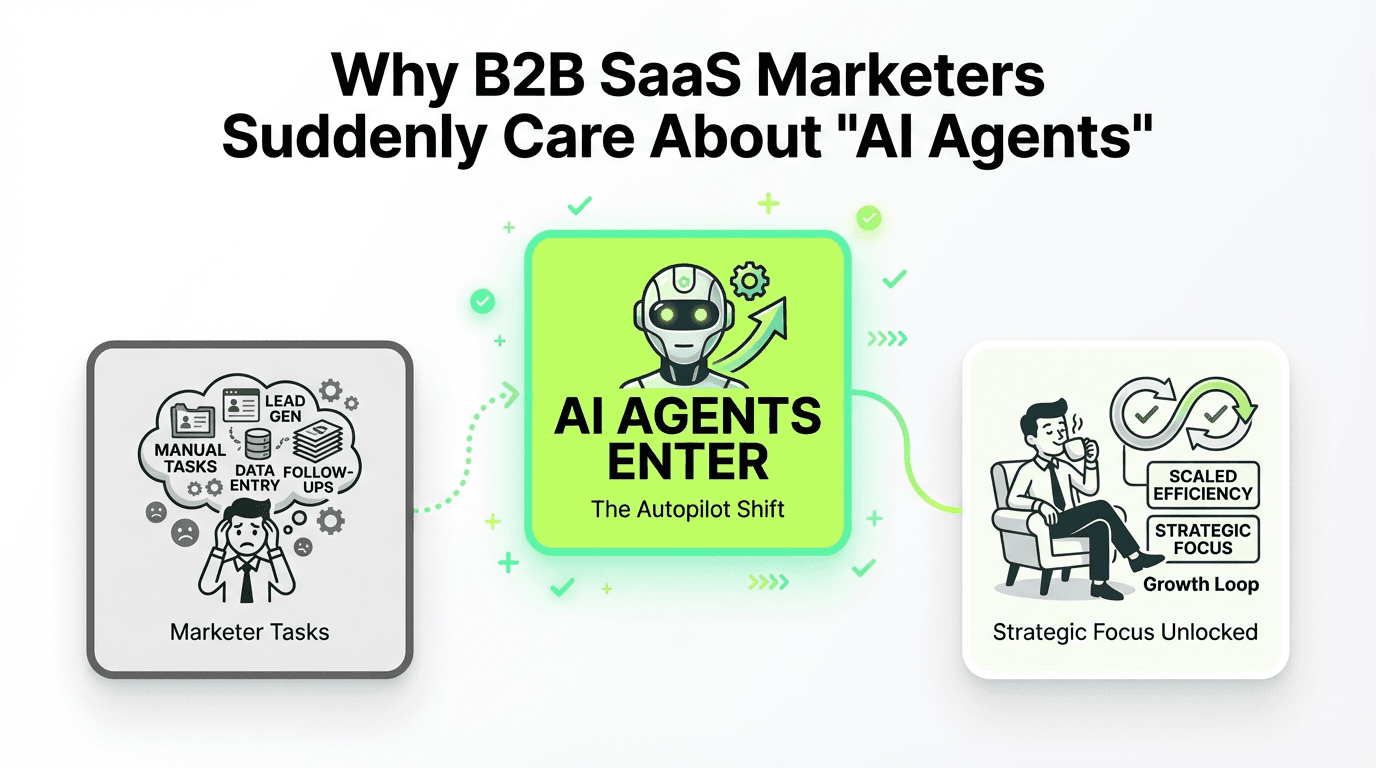
Enter AI agents.
Unlike the assistive AI features you're used to (autocomplete, suggestions, one-off predictions), AI agents represent a fundamental shift toward autonomous workflows. They don't just recommend actions—they observe your data, decide what needs to happen next, and actually execute those actions across your tools. For B2B SaaS marketing teams juggling CRM hygiene, lifecycle nurturing, lead routing, campaign optimization, and reporting, this shift promises something radical: marketing operations that run themselves within guardrails you define.
In this guide, we'll define what AI agents actually are in plain English, show you how they differ from traditional marketing automation, and walk through concrete examples of how AI agents fit into real B2B SaaS marketing workflows. No hype, no jargon—just a practical look at what's possible when you move from building rigid workflows to designing autonomous agents.
What Are AI Agents? A Simple, Marketing-Friendly Definition
Let's cut through the technical noise. Here's a working definition tailored for marketers:
An AI agent is a software entity that can observe data from your marketing and product stack, decide what action to take based on a goal you've given it, and execute those actions across your tools—with minimal human intervention.
Think of it as a digital team member that can read signals, make judgment calls, and do the work, not just suggest what you should do.
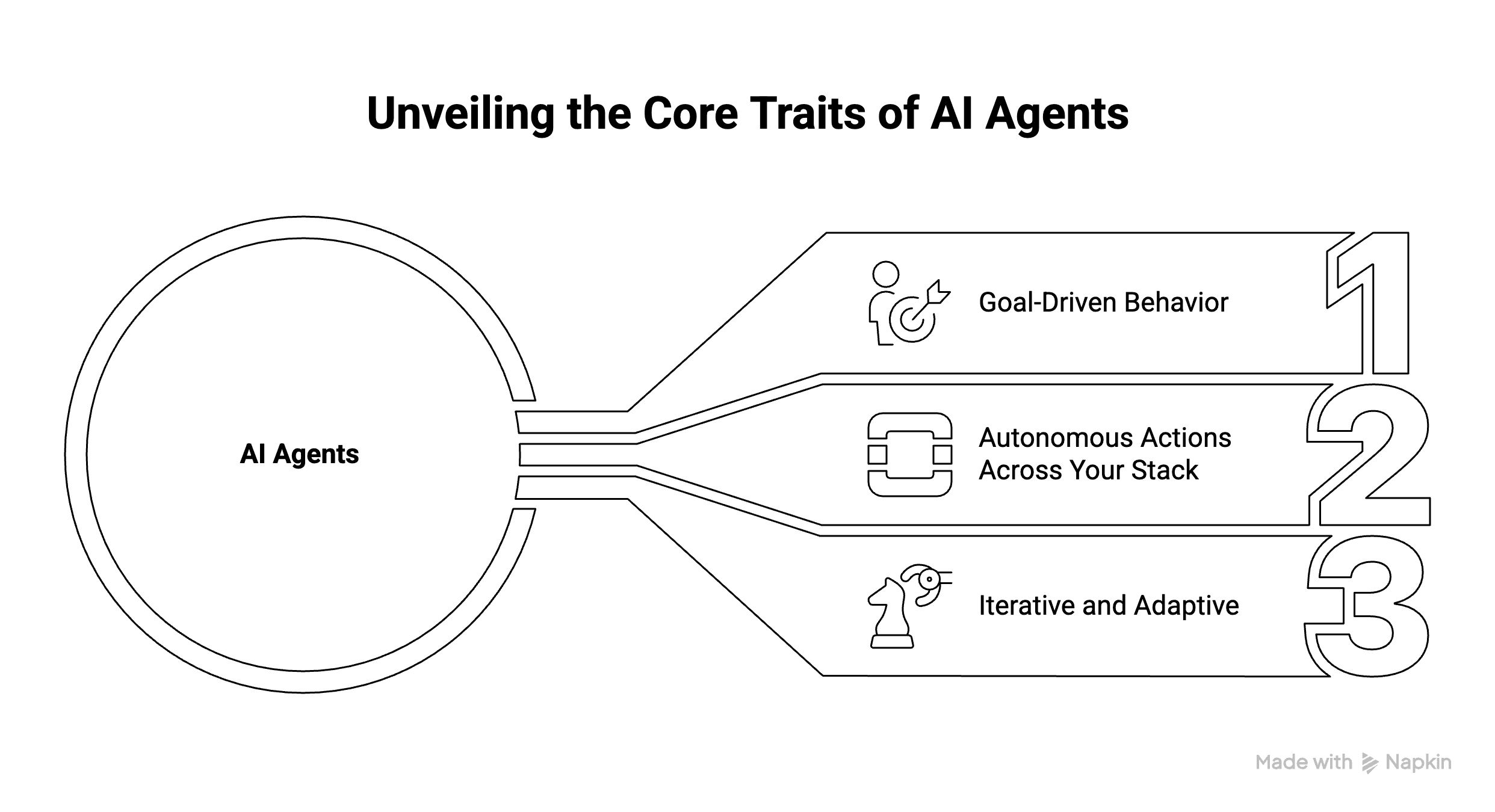
The Three Core Traits of AI Agents in Marketing
To understand what makes something an "AI agent" versus just another automation or AI feature, look for these three characteristics:
1. Goal-Driven Behavior
You don't program every step. Instead, you give the AI agent a clear outcome: "Qualify inbound leads and route them to the right sales rep within 5 minutes" or "Increase trial-to-paid conversion for SMB signups."
The AI agent then figures out how to achieve that goal using the data and actions available to it.
2. Autonomous Actions Across Your Stack
An AI agent doesn't just analyze or recommend—it acts. Specifically, it can:
Read data from multiple sources: CRM records, marketing automation platforms, product usage events, website behavior, enrichment tools
Decide next steps based on patterns, predefined rules, and learned behaviors: score a lead, segment a user, trigger a campaign, create a task for sales
Execute actions automatically: update Salesforce fields, add contacts to HubSpot workflows, send personalized emails, create Slack notifications, adjust ad audiences
This cross-tool orchestration and task automation is what separates agents from single-purpose AI tools.
3. Iterative and Adaptive
Here's where it gets interesting: AI agents can improve over time.
A traditional workflow is static—you build it once, and it runs the same way until you manually redesign it. An AI agent, on the other hand, can monitor outcomes (conversions, response rates, pipeline velocity) and adjust its own tactics: refining lead scoring thresholds, testing different message sequences, or changing routing logic based on what's actually working.
You're not recoding the entire system every time performance dips—you're supervising an AI agent that's constantly tuning itself within boundaries you set.
AI Agents vs. Traditional Workflows: What's the Difference?
A traditional marketing workflow is like a detailed recipe: "If lead source = webinar AND company size > 500, then assign to Enterprise SDR and send Email Template A." It's rigid, explicit, and breaks the moment reality doesn't match your if-then logic.
An AI agent for marketing is more like a skilled assistant: "Here's our ICP definition, our lead routing philosophy, and our response-time goals. Now observe incoming leads, decide who should handle each one, and route them accordingly. Learn from what converts and adjust."
The AI agent can handle ambiguity (what if a lead is 80% ICP fit but showed high intent?), choose from multiple possible actions, and update its approach without you redesigning the entire flow.
How AI Agents Differ from Other "AI" in Marketing
The term "AI" gets slapped on everything in marketing these days, so let's clarify where AI agents actually fit:
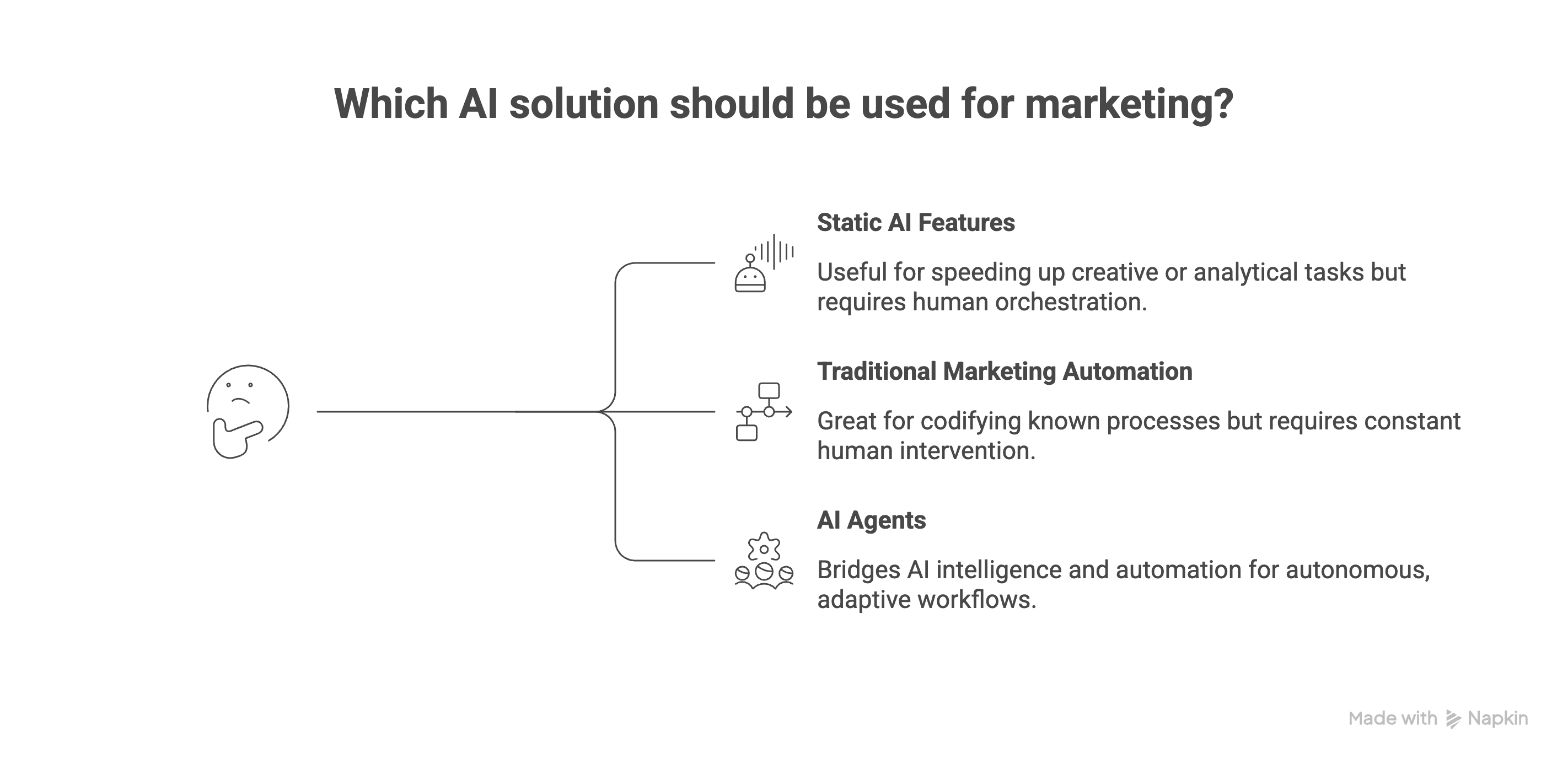
Static AI Features
Examples: AI-generated subject lines, blog post drafters, predictive lead score models baked into your MAP.
Behavior: These are one-shot, narrow-task tools. They generate an output or prediction, then wait for you to do something with it. No memory of broader context, no follow-up actions.
Value: Helpful for speeding up creative or analytical tasks, but you're still the orchestrator.
Traditional Marketing Automation
Examples: HubSpot workflows, Marketo smart campaigns, Zapier zaps.
Behavior: Rule-based, if-this-then-that logic. Powerful when your processes are stable, but brittle and high-maintenance when reality gets messy. Every edge case requires a new branch.
Value: Great for codifying known processes, but requires constant human intervention to update and optimize.
AI Agents for Marketing
Examples: An AI lifecycle agent that owns trial-to-paid nurturing end-to-end, an AI lead operations agent that maintains routing and scoring logic, an AI content distribution agent that optimizes which assets to surface to which segments.
Behavior: Multi-step, cross-tool, goal-oriented. Can interpret ambiguous signals, choose from a menu of possible actions, and refine tactics over time.
Value: Bridges the gap between AI models (which provide intelligence) and automation platforms (which execute actions). AI agents bring both together into autonomous, adaptive workflows.
Think of it this way: AI features give you smarter tools. Automation gives you faster execution. AI agents give you autonomous team members.
Where AI Agents Fit in the B2B SaaS Marketing Stack
AI agents don't replace your existing tools—they orchestrate them. To understand how, let's map agents onto a typical B2B SaaS growth stack.
Your stack probably includes:
Website + product analytics (tracking visitor and user behavior)
CRM (Salesforce, HubSpot CRM)
Marketing automation platform (Marketo, HubSpot, Customer.io, Braze)
Data warehouse or CDP (Snowflake, Segment, Hightouch)
Product analytics (Amplitude, Mixpanel, PostHog)
Sales engagement tools (Outreach, SalesLoft)
AI agents sit on top of this stack, reading data from all these sources and taking actions across them—no more manual CSV exports or fragile Zapier chains.
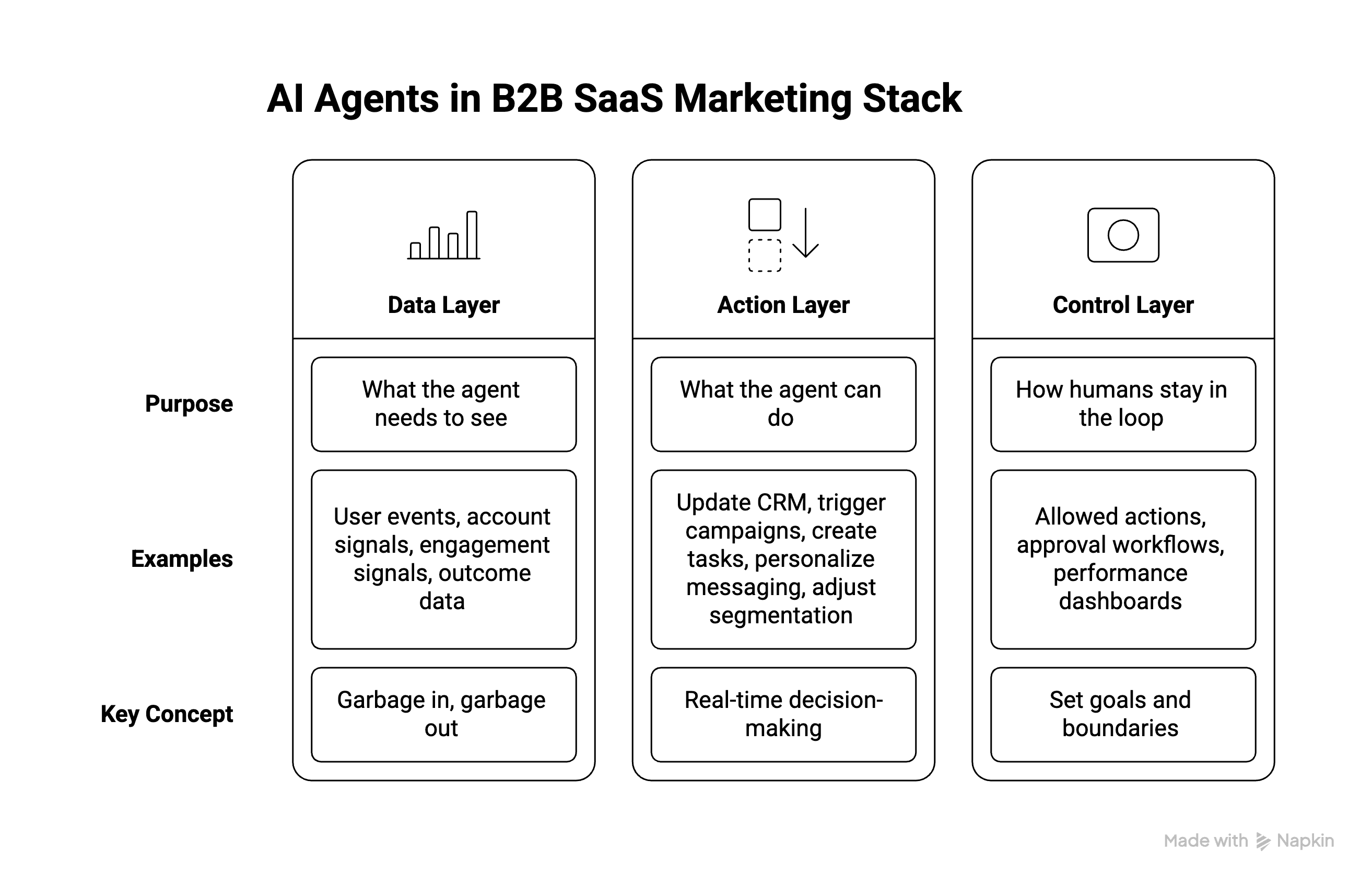
4.1 Data Layer: What an AI Agent Needs to "See"
For an AI agent to make smart decisions, it needs access to:
User and account events: Signups, activations, feature usage, trial expirations, upgrades
Account signals: Company size, industry, tech stack, ICP fit scores from enrichment tools (Clearbit, ZoomInfo, 6sense)
Engagement signals: Email opens and clicks, website page visits, content downloads, demo requests, meeting bookings
Outcome data: SQLs created, opportunities won/lost, churn events, expansion revenue
The richer and cleaner this data layer, the better your AI agents perform. (Garbage in, garbage out still applies.)
4.2 Action Layer: What an AI Agent Can "Do"
Once an AI agent observes the right signals, it can autonomously:
Update CRM fields, scores, and lifecycle stages (e.g., move a lead from MQL to SQL based on product usage)
Trigger campaigns across email, in-app messaging, push notifications, or even sync audiences to ad platforms
Create or update tasks for SDRs and AEs (e.g., "High-intent account just hit pricing page 3x this week—reach out now")
Personalize messaging dynamically by persona, funnel stage, product behavior, or account attributes
Adjust segmentation and routing rules based on performance data
This is where the magic happens: instead of you manually deciding "this lead should get Email Sequence B," the AI agent makes that call in real time, across thousands of leads, 24/7.
4.3 Control Layer: How Humans Stay in the Loop
Autonomy doesn't mean "set it and forget it." You need guardrails:
Allowed and disallowed actions: Define what the AI agent can do independently (e.g., send nurture emails) vs. what requires approval (e.g., change enterprise account routing logic)
Approval workflows: High-impact changes—like adjusting ICP scoring models or pausing campaigns—can require human sign-off
Performance dashboards: Monitor what your AI agents are doing, why they made specific decisions, and how outcomes are trending
Think of it like managing a team: you set goals and boundaries, then supervise performance rather than micromanaging every task.
This is where platforms built specifically for AI agents—like Metaflow AI—shine. Instead of duct-taping together LLMs, automation tools, and data pipelines, you get a unified workspace to design, deploy, and monitor AI agents that orchestrate your entire growth stack. You define the goals and guardrails in natural language; the AI agents handle execution and optimization.
Concrete Examples of AI Agents in B2B SaaS Marketing
Let's make this tangible. Here are three real-world use cases where AI agents can transform how B2B SaaS marketing teams operate.
Example 1: AI Lead Qualification & Routing Agent
Goal: Maximize speed-to-lead and ensure every inbound lead reaches the right owner with zero manual triage.
What it observes:
Form submissions (demo requests, contact sales, content downloads)
Enrichment data (company size, industry, tech stack from Clearbit or ZoomInfo)
Website behavior (pages visited, time on site, repeat visits)
Product signup data (if applicable)
What it does:
Scores the lead and account using a combination of fit (ICP match) and intent (engagement signals)
Decides the next action:
Learns from outcomes: Tracks which leads convert to SQLs and closed-won deals, then adjusts scoring thresholds and routing rules over time (with human oversight)
Before: RevOps spends hours each week manually reviewing leads, updating scores, and fixing mis-routed records.
After: The AI agent handles 95% of routing decisions in under 5 minutes, and the team focuses on refining the ICP definition and coaching reps.
Example 2: AI Lifecycle Nurture Agent (Trials & Freemium)
Goal: Increase trial-to-paid conversion by dynamically guiding users based on their behavior, not static email schedules.
What it observes:
Product events: Features used, features ignored, time to first value, login frequency
Account context: Plan type (free vs. trial), team size, role, use case
Engagement data: Email opens, in-app message clicks, help doc visits
What it does:
Segments users into dynamic journeys:
Chooses the next best action for each user:
Adapts flows based on results: If users who watch a specific onboarding video convert 2x more often, the AI agent prioritizes that content for similar users
Before: Marketers build 5–10 static email drip sequences and hope users fit into one of them.
After: The AI agent tailors the journey for every user in real time, optimizing toward activation and conversion, not email open rates.
Example 3: AI Content Distribution & Experimentation Agent
Goal: Increase pipeline influence from content without marketers manually managing every campaign and A/B test.
What it observes:
Content performance: Which blog posts, whitepapers, webinars, and case studies drive demo requests, trial sign-ups, or product adoption
Segment behavior: Which personas, industries, and funnel stages respond to which topics and formats
What it does:
Dynamically selects content for nurture sequences: Instead of hardcoding "Send Whitepaper X on Day 3," the AI agent chooses which asset to feature based on the recipient's persona, stage, and past engagement
Tests and optimizes delivery: Experiments with subject lines, send times, channels (email vs. in-app vs. Slack), and CTAs
Optimizes toward business KPIs: Focuses on outcomes like MQL→SQL conversion, PQL creation, or pipeline generated—not just vanity metrics like open rates
Before: Content marketers manually A/B test campaigns, wait weeks for results, then rebuild workflows.
After: The AI agent runs continuous micro-experiments and shifts content distribution in real time, accelerating learning cycles from weeks to days.
What are the benefits of AI Agents for B2B SaaS Marketing & Growth Teams
Why should you care about AI agents beyond the cool factor? Here are the tangible benefits:
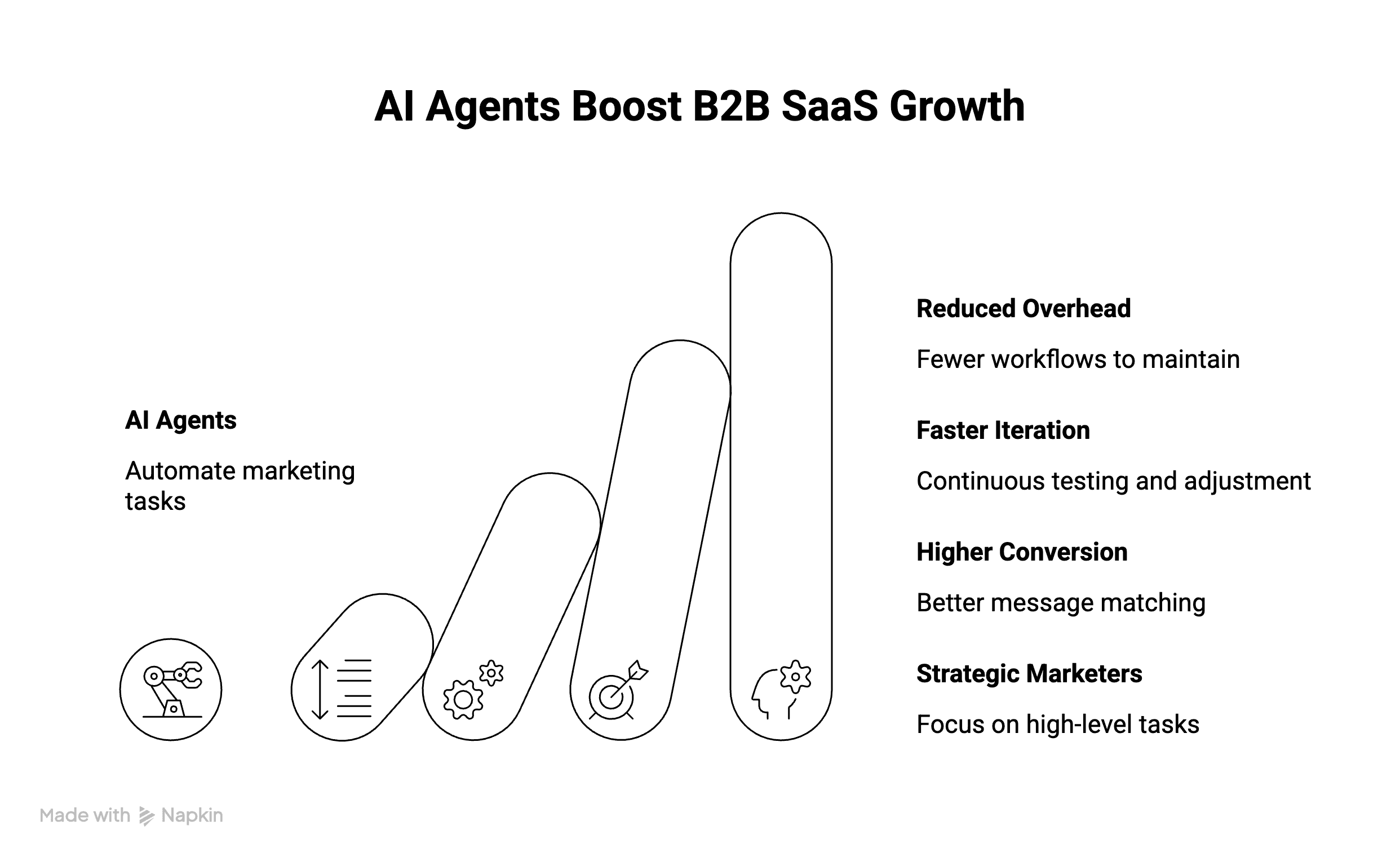
1. Reduced Ops Overhead
Fewer brittle workflows to maintain. Less dependency on RevOps or marketing ops to update logic every time your ICP changes or a campaign needs tweaking. AI agents adapt within the guardrails you set, so your team isn't constantly firefighting broken automations.
2. Faster Iteration and Optimization
AI agents can test and adjust micro-decisions—timing, segments, next actions—far faster than human agents can. What used to take a quarterly planning cycle can now happen continuously in the background.
3. Higher Conversion Across the Funnel
Better matching of message to behavior and stage. Faster response times on high-intent signals (no more leads sitting in a queue for 24 hours). Personalized experiences at scale without manual segmentation.
4. More Strategic Marketers
When AI agents handle execution and optimization, marketers get their time back to focus on what humans do best: strategy, creativity, narrative, experimentation, and cross-functional collaboration.
Before vs. After:
Before: Marketers spend weeks building workflows, then months tweaking them as reality diverges from assumptions.
After: Marketers design goals, constraints, and brand guardrails, then supervise AI agents that handle the execution and continuous optimization.
This is the shift from "marketing technician" to "marketing strategist."
What are the Risks, Limitations, and How to Stay in Control with AI Agents in B2B Saas Marketing
AI agents sound powerful—and they are—but let's be honest about the risks and how to mitigate them.
Risk 1: Data Quality Issues
The problem: Garbage in, garbage out. If your tracking is broken, your enrichment data is stale, or your CRM hygiene is poor, your AI agents will make bad decisions at scale.
Mitigation: Audit your data foundations before deploying AI agents. Invest in clean event tracking, reliable enrichment, and CRM hygiene processes. Start AI agents on high-quality data subsets first.
Risk 2: Over-Automation and Customer Experience Damage
The problem: If you let an AI agent send unlimited emails or make aggressive sales handoffs without constraints, you risk hurting deliverability, annoying prospects, or damaging your brand.
Mitigation: Define strict guardrails: frequency caps, suppression lists, tone-of-voice guidelines, and approval requirements for high-stakes actions. Start conservative and loosen constraints as you gain confidence.
Risk 3: Lack of Explainability
The problem: If your team doesn't understand why an AI agent made a decision (e.g., why this lead was scored down or routed differently), trust erodes fast.
Mitigation: Use platforms that provide decision logs and explainability dashboards. Require AI agents to "show their work"—what data they observed, what logic they applied, what action they took, and why.
Risk 4: Security Concerns
The problem: Granting AI agents access to sensitive customer data and the ability to execute actions across your stack introduces potential security vulnerabilities if not properly managed.
Mitigation: Implement role-based access controls, encrypt sensitive data, audit AI agent actions regularly, and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations. Work with platforms that prioritize enterprise-grade security and provide comprehensive audit trails.
How to Stay in Control
Start narrow: Pick one high-leverage, low-risk use case (e.g., trial nurture for SMB segment in one region)
Human-in-the-loop at first: Require approval on big decisions until you trust the AI agent's judgment
Define success metrics carefully: Don't just optimize for "more emails opened"—tie AI agent performance to business outcomes like conversion rates, pipeline velocity, or revenue
Review regularly: Weekly check-ins on AI agent decisions and outcomes, at least initially
How AI Agents Work: Understanding the Technology
To effectively deploy and manage AI agents, it helps to understand how they work under the hood. At their core, AI agents leverage large language models (LLMs) and generative AI to process information and make decisions.
The Foundation: Large Language Models
AI agents are powered by large language models—sophisticated artificial intelligence systems trained on vast amounts of data. These foundation models enable AI agents to understand natural language, interpret context, and generate human-like responses. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, language models can handle ambiguity and adapt to new situations they haven't explicitly been programmed for.
Task Decomposition: Breaking Down Complex Tasks
One of the key capabilities that makes AI agents effective is task decomposition. When you give an AI agent a complex task like "optimize our trial-to-paid conversion funnel," it breaks this down into smaller, manageable subtasks:
Analyze current conversion rates by segment
Identify drop-off points in the user journey
Determine which specific tasks to prioritize
Execute related tasks like updating email sequences or adjusting in-app messaging
Monitor results and iterate
This ability to decompose complex tasks into actionable steps is what separates AI agents from simpler AI assistants that can only handle specific tasks.
Beyond Natural Language Processing
While natural language processing allows AI agents to understand instructions and communicate findings, modern AI agents go beyond natural language understanding. They can:
Execute code generation to create custom scripts and integrations
Apply action rules based on real-world conditions
Calculate utility functions to determine the best course of action
Assign utility values to different options and choose the optimal path
How Do AI Agents Work in Practice?
Here's a simplified view of how AI agents work when handling a marketing task:
Perception: The AI agent observes data from your marketing stack using APIs and integrations
Decision-making: Using its language model and predefined rules, it evaluates options and determines the best action
Action: The AI agent executes the chosen action (sending an email, updating a CRM field, routing a lead)
Learning: The AI agent monitors outcomes and adjusts its approach based on what works
This cycle repeats continuously, allowing the AI agent to handle repetitive tasks while improving its performance over time.
AI Agents Examples: What are some Real-World Applications Beyond Marketing
While we've focused on B2B SaaS marketing, it's worth understanding how AI agents are being deployed across different domains. These AI agents examples illustrate the versatility of the technology:
Customer Management & Support
AI agents are revolutionizing customer management by handling routine inquiries, routing complex issues to human agents, and proactively reaching out to at-risk customers. They can analyze sentiment, identify escalation triggers, and maintain context across multiple interactions—all while learning from each customer interaction.
Code Generation & Development
In software development, AI agents assist with code generation, debugging, and documentation. They can understand requirements in natural language, generate functional code, suggest optimizations, and even identify potential security concerns before deployment.
Task Automation Across Industries
From finance to healthcare, AI agents are handling repetitive tasks that previously required human attention: processing invoices, scheduling appointments, managing inventory, and coordinating logistics. The key is that these aren't simple automated scripts—they're intelligent agents that can adapt to exceptions and unusual circumstances.
How to Create an AI Agent: Getting Started
If you're wondering how to create an AI agent for your specific needs, here's what you need to know about the process:
Option 1: Build from Scratch (Technical Route)
Building an AI agent from scratch requires:
Technical expertise: Understanding of language models, API integrations, and agent architecture in AI
Infrastructure: Hosting for your language model or access to AI services like OpenAI or Anthropic
Data pipelines: Systems to feed data to your AI agent and execute its decisions
Monitoring: Tools to track AI agent performance and catch errors
This approach gives you maximum control but requires significant engineering resources and ongoing maintenance.
Option 2: Use an AI Agent Platform (Practical Route)
For most B2B SaaS marketing teams, using a specialized platform is more practical. Platforms like Metaflow AI allow you to create an AI agent without deep technical expertise:
Natural language configuration: Describe what you want the AI agent to do in plain English
Pre-built integrations: Connect to your existing marketing stack without custom API work
Visual workflow designers: Map out decision logic without writing code
Built-in guardrails: Security, compliance, and approval workflows included
Key Considerations When Creating an AI Agent
Regardless of which route you choose, consider:
Scope: Start with a specific task rather than trying to automate everything
Data access: Ensure your AI agent can access the data it needs to make decisions
Action permissions: Define what the AI agent can do autonomously vs. what requires approval
Success metrics: Determine how you'll measure whether the AI agent is working
Iteration plan: Build in regular review cycles to refine the AI agent's behavior
How to Get Started with AI Agents: A Practical Playbook
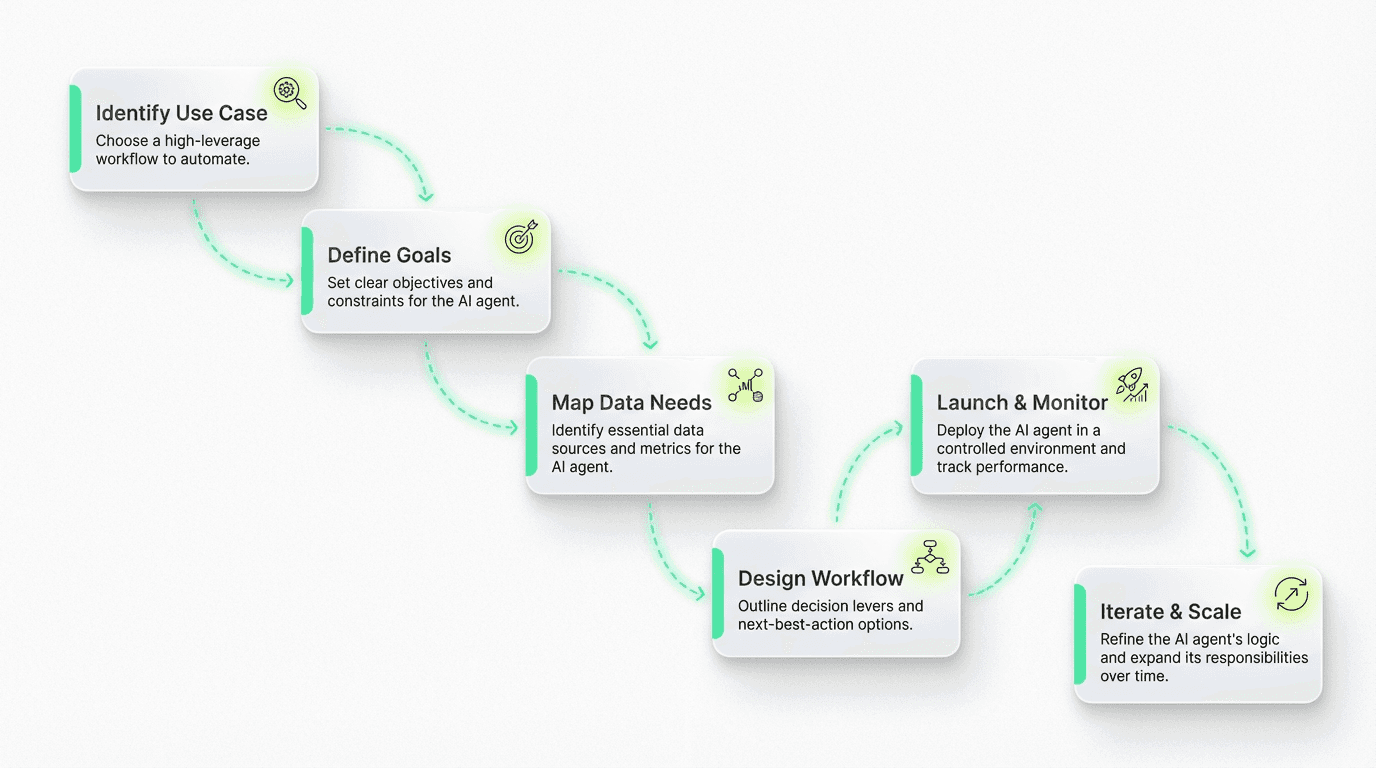
Ready to move from theory to practice? Here's a step-by-step framework to launch your first AI agent.
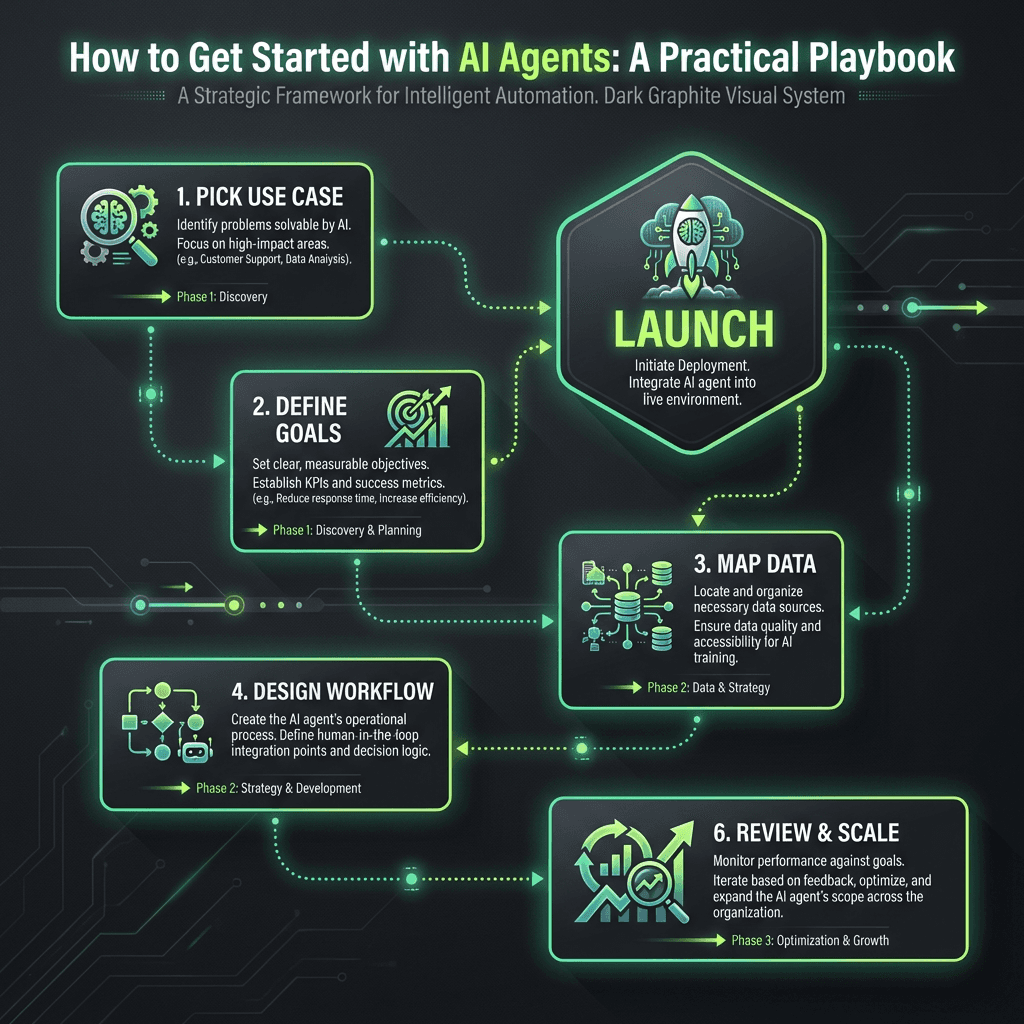
Step 1: Pick One Clear, High-Leverage Use Case
Don't try to automate everything at once. Choose a single workflow where:
You have clean, reliable data
The outcome is measurable
The current process is painful or time-consuming
Example: "Automate trial nurture for self-serve signups from SMB companies in North America."
Step 2: Define the Goal and Constraints
Be explicit about what success looks like and what the AI agent is not allowed to do.
Goal example: Increase trial→paid conversion by 15% within 90 days.
Constraints example:
Only use email and in-app messaging (no sales handoffs yet)
Respect brand tone and voice guidelines
Do not overwrite manually updated CRM fields
Cap email frequency at 3 per week per user
Step 3: Map the Data the AI Agent Needs
List every data source and event the AI agent should observe:
Product events: signup, activation, feature usage, trial expiration
User traits: role, company size, use case
Engagement: email opens, in-app clicks, help doc visits
Ensure this data is flowing reliably into a place the AI agent can access (your CDP, data warehouse, or marketing automation platform).
Step 4: Design the Initial Policy / Workflow
Instead of building 20 branches of if-then logic, define a few decision levers and next-best-action options the AI agent can choose from.
Decision levers:
Stage classification: New, Activated, At-Risk, Ready to Upgrade
Engagement level: High, Medium, Low
ICP fit: Strong, Moderate, Weak
Next-best-action options:
Send onboarding content
Trigger feature spotlight
Offer setup call
Send upgrade prompt
Alert sales rep
The AI agent decides which action to take based on the user's current state and goal.
Step 5: Launch in a Sandbox or Small Cohort
Don't go live across your entire database on day one. Start with:
A small segment (e.g., one region, one persona, or 10% of traffic)
A controlled environment (e.g., a test CRM instance or a staging MAP)
Monitor closely for the first few weeks.
Step 6: Review, Refine, and Scale
Set up a weekly review cadence:
What decisions did the AI agent make?
What were the outcomes (conversion rates, engagement, pipeline)?
Were there any errors or unexpected behaviors?
Refine the AI agent's logic, expand constraints, or add new actions as you gain confidence. Gradually widen the scope to more segments, more actions, and more autonomy.
This is where platforms like Metaflow AI become invaluable. Instead of duct-taping together LLMs, APIs, and automation tools, you get agentic marketing platform designed specifically for growth marketing. You define goals and guardrails in plain English, the platform handles orchestration across your stack, and you monitor AI agent performance in a unified dashboard. It's the difference between spending months on infrastructure and launching your first AI agent in days.
From Workflows to Agents: The Future of B2B SaaS Marketing
For the past decade, B2B SaaS marketers have been workflow designers—building elaborate if-then logic trees in HubSpot, Marketo, and Zapier, then constantly maintaining them as reality shifts.
AI agents flip that model.
Instead of designing every step, you design goals and guardrails. You tell an AI agent what success looks like, what data to observe, what actions it's allowed to take, and what constraints to respect. Then you supervise, refine, and scale.
Over the next few years, the competitive edge in B2B SaaS marketing will come from two things:
How well you instrument your data. Clean, real-time data on user behavior, account fit, and engagement signals is the fuel for intelligent AI agents.
How thoughtfully you give AI agents scoped autonomy. The best teams won't hand over the keys blindly—they'll start narrow, define clear success metrics, and gradually expand AI agent responsibilities as trust builds.
This isn't about replacing marketers with robots. It's about freeing marketers from repetitive orchestration work so they can focus on what humans do best: strategy, creativity, experimentation, storytelling, and building relationships in the real world.
The question isn't whether AI agents will reshape B2B SaaS marketing—it's whether your team will lead that shift or scramble to catch up. Understanding what are AI agents and how do they work is the first step. Learning how to create an AI agent tailored to your needs is the next.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Audit one funnel in your stack (trial-to-paid, lead-to-SQL, or content-to-pipeline) and document where an AI agent could take over repetitive decisions and actions. Map the data, the goal, and the constraints. That's your blueprint.
If you want to see what this looks like in practice—where AI agents orchestrate your entire growth stack without the usual integration headaches—explore
Metaflow AI is an agent builder designed specifically for growth teams who want to move fast, experiment freely, and scale what works—without becoming automation engineers.
FAQs
What is an AI agent in marketing?
An AI agent in marketing is software that can observe customer and campaign data, decide what to do next, and take actions across your tools (CRM, MAP, product, analytics) to achieve a goal such as qualifying leads or driving upgrades.
How are AI agents different from traditional marketing automation?
Traditional automation is rule-based and static (if-this-then-that workflows). AI agents are goal-driven and adaptive: they interpret signals like behavior and fit, choose from multiple possible actions, and adjust tactics over time without you rebuilding flows.
How do AI agents fit into a B2B SaaS marketing stack?
AI agents sit on top of your existing stack—CRM, marketing automation, product analytics, data warehouse—and orchestrate it. They read data, decide on the next best action, then update records, trigger campaigns, or create tasks for sales.
What are the main use cases of AI agents for B2B SaaS marketers?
High-impact use cases include lead qualification and routing, trial/freemium lifecycle nurturing, churn-risk detection and save plays, account-based engagement, and content or campaign optimization based on pipeline and revenue impact.
Do AI agents replace marketers or marketing ops?
No. AI agents automate repetitive, operational decisions. Marketers and ops teams stay responsible for strategy, goals, guardrails, messaging, and reviewing performance.
What data does an AI agent need to work well?
AI agents need reliable customer and account attributes (ICP traits, firmographics), engagement data (email, website, ads, meetings), product usage events, and revenue outcomes (SQLs, opportunities, closed-won/lost).
What are the risks of using AI agents in marketing?
Key risks include acting on bad data, over-automation that harms user experience, and lack of visibility into why decisions were made. You manage this with guardrails, limited scopes, approvals for high-impact actions, and regular reviews.
How can B2B SaaS teams start using AI agents?
Start with one focused use case (for example, trial nurture for a single segment), define a clear KPI, map the data and tools the agent can access, set constraints on allowed actions, run on a small cohort, then scale as results and trust improve.
Similar Posts

The Actually Easy Guide to Building Claude Skills

A Practical Guide to Building AI Workflows for B2B SaaS Marketing

25 Questions That Build a Real AI Marketing Strategy (Not Just an AI Stack)

Notion Agents vs Metaflow AI Agents: Building an AI Workflow That Works for You

How to Build AI Agents that actually gets stuff done

AI Content Repurposing with Customizable Prompts: Build Your Own Repurposing Tool with Metaflow AI

Account Intelligence Automation: How to Build AI Research Agents for ABM

Building AI Agents for Multi-Threading in ABM: Buying Committee Automation

How to Build an AI Intent Signal Aggregation Agent for ABM

AI Workflow Builder: How to Quickly Build Automated Growth Engines
SOLUTIONS
COMPARISON GUIDES
GET STARTED











